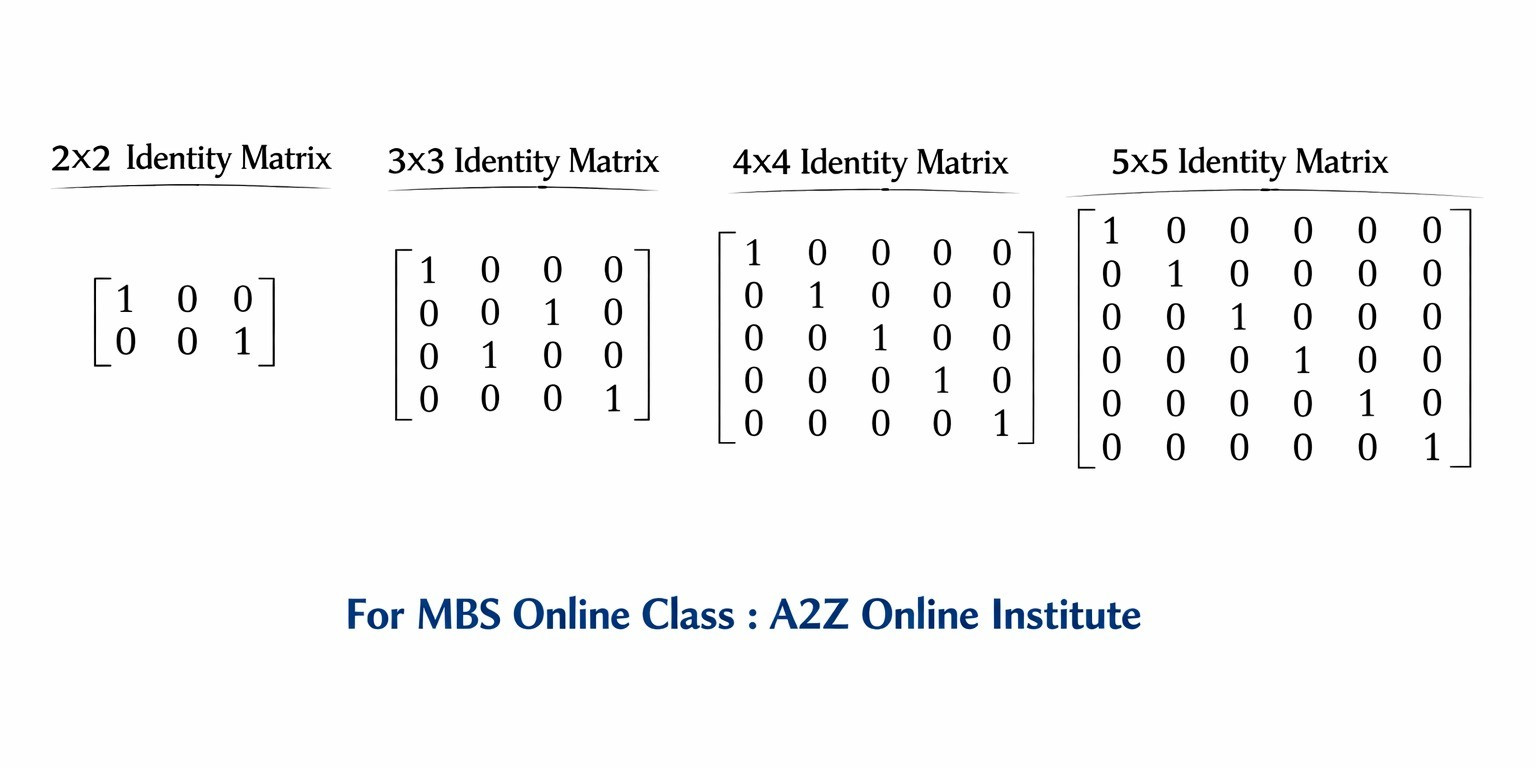
Identity Matrix: Meaning, Definition, and Importance
Definition of Identity Matrix
An identity matrix is a square matrix in which the elements along the principal (main) diagonal are all equal to one, while all other elements are zero. It is generally represented by the symbol I or Iₙ, where n indicates the order of the matrix.
Properties of Identity Matrix
-
It exists only as a square matrix.
-
For any matrix of the same order, multiplication with an identity matrix leaves the matrix unchanged.
-
For a given order, there is only one identity matrix.
-
The identity matrix is self-inverse, meaning its inverse is the matrix itself.
-
It plays a key role in defining and understanding matrix inverses.
It exists only as a square matrix.
For any matrix of the same order, multiplication with an identity matrix leaves the matrix unchanged.
For a given order, there is only one identity matrix.
The identity matrix is self-inverse, meaning its inverse is the matrix itself.
It plays a key role in defining and understanding matrix inverses.
Importance of Identity Matrix
The identity matrix is widely used in various fields such as mathematics, economics, engineering, statistics, and computer science. It is essential in solving systems of linear equations, performing matrix transformations, and understanding linear mappings. Because of its unique properties, it serves as a foundation for many advanced topics in linear algebra.
Conclusion
The identity matrix is a simple yet powerful mathematical concept. Its role as the multiplicative identity in matrix algebra makes it indispensable for both theoretical understanding and practical applications in higher-level mathematics and related disciplines.


0 Comments